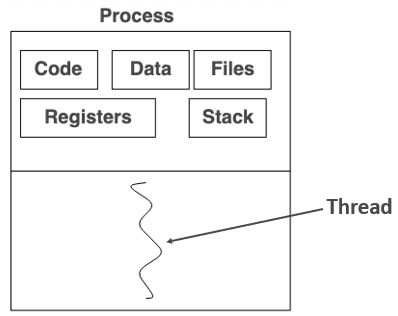
Process
- An independent program execution unit.
- Runs in its own memory space.
- Can communicate with other processes using inter-process communication mechanisms.
- Requires more overhead to create and manage than threads.
- It has its own copy of the data section, heap and stack.
- Provides better isolation and protection between applications and services.
- Can run on different processors or cores in parallel, providing true parallelism.
- Switching between processes is more expensive and time-consuming than switching between threads.
- Used for running multiple independent applications or services simultaneously.
- Can be managed and scheduled by the operating system using process scheduling algorithms.
Thread
- A subset of a process, sharing memory and resources with other threads within the same process.
- Runs in the same memory space as the parent process.
- Can communicate with other threads within the same process directly through shared memory or synchronisation primitives.
- Requires less overhead to create and manage than processes.
- Shares the data section, heap and stack with other threads in the same process.
- Provides more efficient and faster execution by leveraging shared memory and communication between threads.
- Can run on a single processor or core, providing concurrency but not true parallelism.
- Switching between threads is less expensive and faster than switching between processes.
- Used for running multiple concurrent tasks within a single application or service.
- Can be managed and scheduled by the operating system using thread scheduling algorithms.
Side-by-Side comparison of process and Thread
| Process | Thread |
|---|---|
| A process is a program in execution that has its own memory space, resources, and scheduling information. | A thread is a lightweight sub-process that shares the same memory space and resources as its parent process. |
| Processes are independent and isolated from each other. They cannot directly access each other’s memory space and resources. | Threads are not independent and can access shared resources and memory space with other threads of the same process. |
| Each process has its own virtual address space, file descriptors, and system resources like I/O operations, network connections, and signals. | Threads share the same virtual address space, file descriptors, and system resources as the parent process. |
| Processes communicate with each other using interprocess communication (IPC) mechanisms like pipes, sockets, and shared memory. | Threads communicate with each other using shared variables and synchronization primitives like locks and semaphores. |
| Processes have a larger overhead in terms of memory consumption and context switching compared to threads. | Threads have a smaller overhead in terms of memory consumption and context switching compared to processes. |
| Processes are more robust and reliable compared to threads since a crash in one process does not affect the others. | Threads are less robust and reliable compared to processes since a crash in one thread can affect the entire process. |
| Processes are used to run different programs simultaneously, and each process provides its own execution environment. | Threads are used to improve the performance of a program by parallelizing its execution and exploiting the benefits of multitasking. |